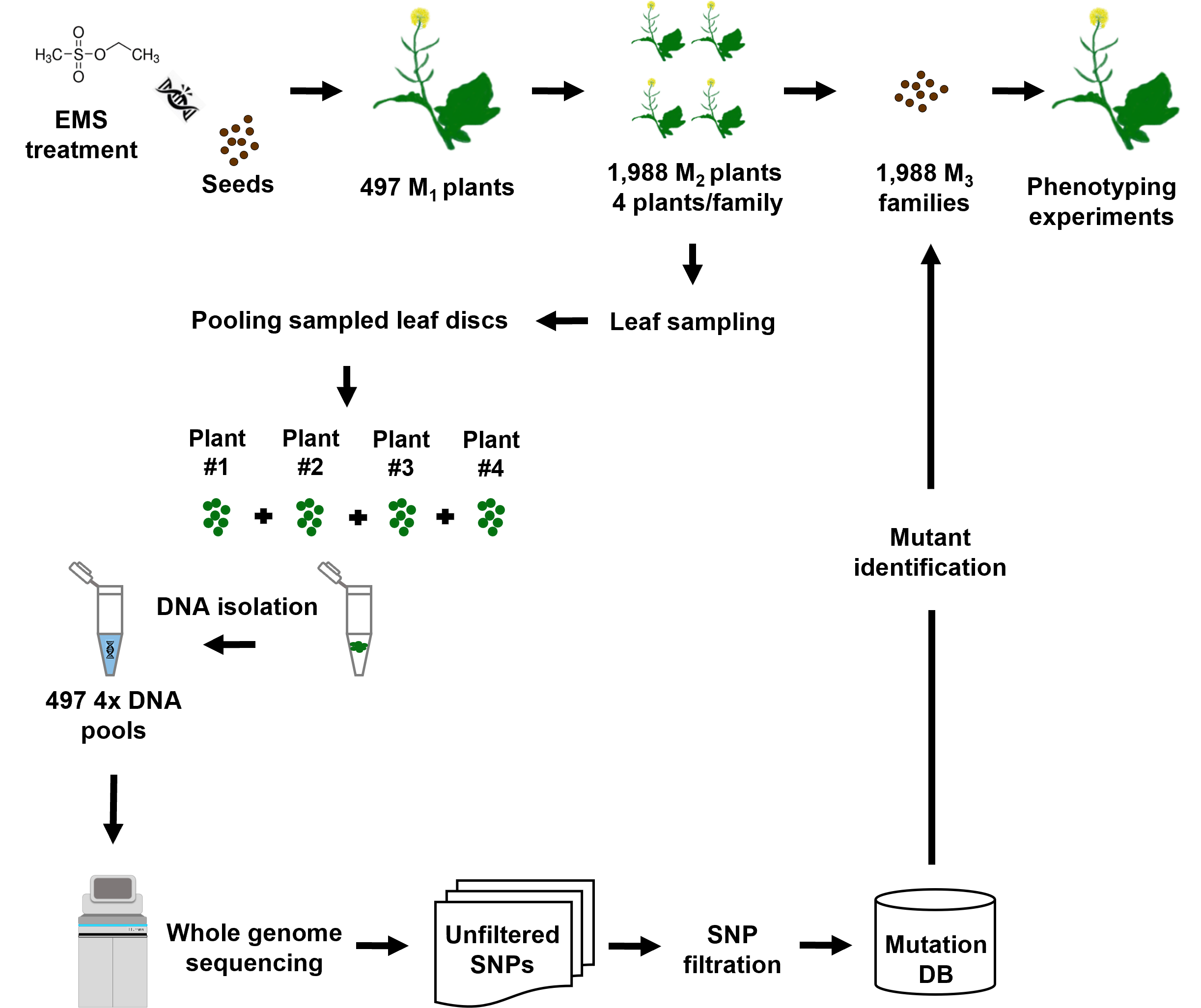
Workflow of the mutant detection procedure following the established TILLING by whole genome sequencing (TbyWGS) approach.
Mutations were detected in an EMS mutagenized Express617 population using a whole genome sequencing approach. M1 plants originating from EMS treated seeds were grown for production of M2 seeds. 1,988 single M2 plants originating from 497 M1 plants were grown and genomic DNA of four M2 plants/family was bulked to produce fourfold (4x) DNA pools. Each 4x pool was sequenced on the Illumina NovaSeq 6000 platform. Raw SNPs were filtered based on C→T and G→A transitions possessing read depth (DP)≥10, allele depth (AD)=12.5%-60% and quality controlled for mapping quality (MQ)≥30. Mutation effects from resulting high confidence SNPs were predicted. Putative functional mutants from individual pools were merged in a user accessible format.
Jhingan, Srijan, Avneesh Kumar, Hans-Joachim Harloff, Felix Dreyer, Amine Abbadi, Katrin Beckmann, Christian Obermeier, and Christian Jung. "Direct access to millions of mutations by Whole Genome Sequencing of an oilseed rape mutant population." The Plant Journal (2022). https://doi.org/10.1111/tpj.16079